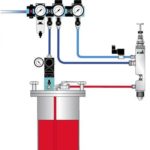
What is salt spray test?
Salt spray test is an accelerated corrosion resistance evaluation method that artificially simulates atmospheric salt environment. It is generally used to evaluate, screen and compare materials (surface film layer) or surface treatment processes. Through salt spray test, the areas and parts of potential problems from product can be determined, the deficiencies in quality control can be found, and design defects can be found.
Salt spray test is to atomize a certain concentration of salt water then spray it in a closed constant temperature chamber. The corrosion resistance of the tested sample is reflected by observing the changes after the tested sample is placed in the chamber for a period of time.
Comparing to the natural environment, salt concentration of chloride in the salt spray environment is several times or dozens of times that of the salt spray content in general natural environment. The corrosion rate can be greatly increased by conducting salt spray tests on products, and the time to obtain results is also greatly shortened. It may take 1 year for a product sample to be corroded in a natural exposure environment, but it only takes 24 hours to get similar results in an artificial simulated salt spray environment.
Principle of salt spray test
The detailed principles of salt spray test are summarized as follows:
1. Penetration and adsorption
① The corrosion of metal materials by salt spray is caused by the electrochemical reaction between chloride ions penetrating the oxide layer and protective layer on the metal surface and internal metal.
② Chloride ions contain certain hydrates and are easily adsorbed in the pores and cracks on the metal surface, displacing and replacing the oxide layer.
③ Change insoluble oxides into soluble chlorides, turning the passivated surface into an active surface. This causes extremely bad adverse reactions to the product.
2. Electrochemical corrosion
① The corrosion of metal materials by salt spray is mainly caused by the electrochemical reaction of the conductive salt solution penetrating into the metal, and metal as the anode dissolves to form new compounds, namely corrosive products.
② The same is true for the metal protective layer and the organic material protective layer. When the salt solution as an electrolyte penetrates into the interior, a micro-battery with the metal as the electrode (anode) and the metal protective layer or organic material as the other electrode (cathode) will be formed.
③ Chloride ions play a major role in the process of salt spray corrosion damage. It has a strong penetrating ability and can easily penetrate the metal oxide layer into the metal, destroying the metal passive state. At the same time, chloride ions have very small hydration energy and are easily adsorbed on the metal surface, replacing the oxygen in the oxide layer that protects the metal, causing the metal to be damaged.
3. Oxygen content and internal stress
① Oxygen can cause the depolarization process of the metal surface and accelerate the dissolution of the anode metal. Due to the continuous spraying during the salt spray test, the salt liquid film that continuously settles on the sample surface keeps the oxygen content close to saturation.
② The formation of corrosion products causes the volume of salt solution that penetrates into the metal defects to expand, thereby increasing the metal internal stress which lead to stress corrosion, and causing the protective layer to bulge.
It should be noted that because the salt spray test is an environmental test that mainly uses artificial simulated salt spray environmental conditions created by salt spray test equipment to assess the corrosion resistance of products or metal materials, it also has certain limitations. It only emphasizes the environmental factors of the marine environment or salty air, not all natural salt environmental conditions. At present, the salt spray test is an effective method for the industry to inspect the quality and defects of materials and evaluate corrosion resistance.